Introduction to Solar Electricity

The climate crisis, the rapid depletion of fossil fuels, the degradation of the environment, and the soaring electricity prices are just some reasons why solar energy has been enjoying explosive growth in the country.
The energy from the sun is natural, unlimited, and clean as it emits no harmful gases that poison the air or contaminate the environment. It also offers excellent value because the electricity that solar panels generate is sometimes cheaper than the power coming from the grid. That makes solar energy an excellent alternative power source for our homes and businesses.
What Is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the power that comes from the sun. Solar panels work by capturing the sun’s rays that strike their surface.
Using the sun’s radiance has a long history, starting as early as the 7th century BC when humans lit fires using magnifying glasses.
In 1839, Edmond Becquerel, a 19-year-old French physicist, discovered the photovoltaic effect, that is, the creation of voltage or electric current when a material is exposed to light.
In 1873, Willoughby Smith discovered the photo-conductive ability of selenium. This led to a cascade of discoveries, with Charles Fritts introducing the first solar or PV cells to the world by using selenium on a thin layer of gold. This is the reason why some historians gave Fritts credit for the invention of solar cells.
The giant leap to the PV panels as we know them today came from the works of scientists Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson at Bell Labs in 1954. Their efforts produced the first device that converted solar energy into electricity.
Although no one man can lay claim to the honor of inventing the solar panel, the contribution by several individuals created the foundation for what will, later on, become the world’s fast-growing source of clean, renewable energy.
Since its beginnings, the technology behind solar power had advanced tremendously, making solar energy one of the best sources of renewable power that we know, and benefit from, today.
How Does Solar Power Work?
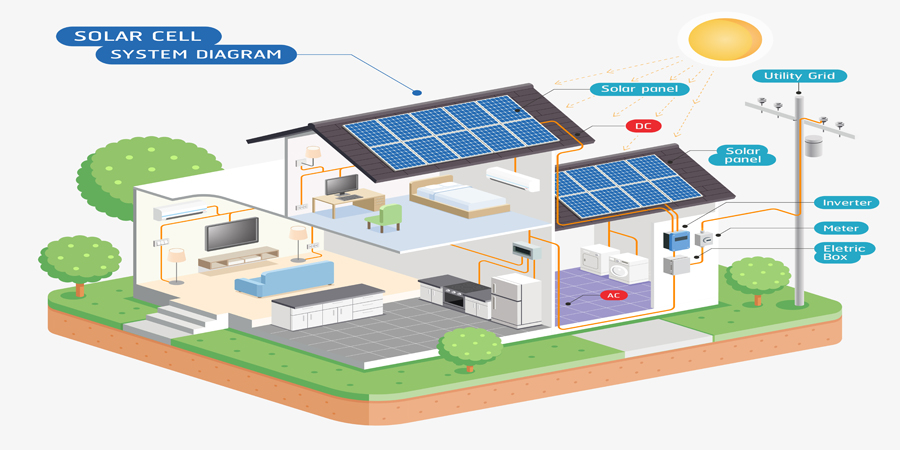
The sun releases tiny packets of energy called photons. These photons strike the earth and, if harnessed, an hour’s worth of sunlight can generate enough electricity that can cover the world’s needs for a year.
The sun’s energy turns into solar power with the use of solar or photovoltaic (PV) panels. The solar cells inside a solar panel capture sunlight and transform the energy they absorb into direct current (DC) electricity. However, US households usually accept only alternating current (AC) electricity, so the DC electricity should be converted into AC power. That’s the job of the solar inverter. It turns DC electricity into the type of current our homes can use.
Solar Cells 101: Learning The Basics
A solar panel is a major component of a solar system and is the one responsible for generating clean energy from sunlight. Inside the PV panels are smaller units called solar cells. These cells absorb the energy from the sun’s rays and turn it into electricity.
Leveraging The Photovoltaic Effect
So now we know that we have an unlimited power source coming from the sun. But to harness all the solar power the sun has to offer and turn it into usable electricity, there should be a way to capture all that radiant energy.
This is where solar panels come in. They work by converting the sun’s energy into solar electricity. But not all solar panels are the same. They vary according to the materials used, their appearance, performance, and price.
The three major types of solar panels are:
- Monocrystalline panels: The PV cells in monocrystalline panels are cut from a single silicon crystal, giving them a dark, uniform appearance and round edges. Due to the purity of the silicon used, they are the most efficient type of solar panels.
- Polycrystalline panels: Unlike their monocrystalline counterparts’ dark, uniform appearance, polycrystalline panels have a blue, speckled look. They’re made by melting fragments of silicon that are poured into a mold and then cut into wafers. The manufacturing process is cheaper but tends to result in panels with lower efficiency than monocrystalline ones.
- Thin-film panels: While monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar modules come from silicon alone, various materials are used to create thin-film panels. They are the least efficient among the different types of modules.
Harnessing The Power Of Inverters
Solar panels work by turning sunlight into electricity. But without a solar inverter, the energy captured by the panels can’t be used to power your home, which usually accepts only AC electricity. That makes the inverter another integral component of a solar energy system. The main job of this equipment is to turn the DC current produced by the solar panels into household-friendly AC electricity.
Inverters come in different types, and the basic ones are:
- String inverter: This is the most common and more popularly used type of inverter, where a string, or group, of solar panels is connected to a single inverter.
- Microinverter: Unlike in a string inverter where the solar panels are connected to one central inverter, a microinverter is installed on each module.
- Power optimizer: A power optimizer is not really an inverter but instead is a component that can be combined with a solar panel to make the solar energy system more efficient. It works by optimizing the electricity voltage, which makes it easier for the inverter to turn the DC power into AC electricity
Drawing More And Giving Back
Using solar panels for electricity generation not only reduces your carbon footprint but also offers some financial benefits. One way to get money into your pocket when you use solar energy is through net metering.
Also called net energy metering (NEM), net metering is a billing mechanism that allows solar energy consumers to feed excess electricity back into the grid and get credits on their utility account in return.
What does this mean for you? Well, the amount of electricity generated by your solar energy system is not constant throughout the day and the various seasons of the year. With net metering, when your solar power installation’s electricity production exceeds what you need, the surplus goes back to the grid. In return, you earn credits on your utility account for the electricity you contributed.
You can use those credits to offset the power you draw from the network when your solar energy system doesn’t produce enough power to cover your needs. This situation usually happens at night when your modules no longer generate energy, but you consume more electricity because that’s the time when most household members are at home. Your utility then bills you only for the “net” electricity you used.
Living Off The Grid
Most homes that use solar energy remain connected to the utility grid, or what is known as a grid-tied solar power system. With a grid-tied system, you rely on solar energy to power your home when the solar panels produce sufficient electricity for your household’s requirements and draw power from the network when there’s a shortfall in your system’s production.
In contrast, an off-grid solar installation is a stand-alone system. The electricity it provides comes solely from the output of the PV panels, and your home is not connected to the utility network in any way. Since the system is independent of the electricity grid, it requires battery storage.
In a grid-connected system, the power generated by the panels goes into the inverter, which then sends it into the grid for credits. Meanwhile, when you go off the grid, the DC electricity from the modules goes into the batteries. You can then use the stored energy when your panels are not producing enough electricity for your needs.
Benefits of Going Solar
Apart from saving the environment from further degradation, shifting from fossil fuels to this clean and green power source will also benefit your pocket. Here are some of the reasons that make solar energy a good investment.
Contribute To Saving The Environment
Because solar panels generate electricity without releasing harmful gases into the atmosphere, they don’t contribute to global warming. Moreover, by supplementing the electricity we get from the grid, they reduce our reliance on fossil fuels that produce greenhouse gases and particulates that cause pollution.
Save On Electricity Bills
Electricity from the grid isn’t cheap. In 2020, the average rate of electricity in the U.S. was 13.20¢ per kWh. Compare that with the cost of electricity from solar, which can go as low as $0.06 if present trends continue. That’s a lot of savings on your utility expenses.
Property Value Appreciation
Studies show that, on average, homes with solar panels sell 4.1% more than those without a PV system. A simple calculation will show that with this figure, a house with a value of $226,300 can potentially gain a premium amounting to $9,274.
Switching To Solar Power
Estimate Costs Involved
Switching to solar energy will involve a significant capital outlay. You’ll be able to recoup your expenses over time through the savings on your electricity bills, though, and some incentives and rebates will lessen the initial financial investment.
The majority of the expenses go to the purchase and installation of the solar modules. A 5 kW energy system costs around $3-$5 per watt, which means you’ll need around $15,000-$25,000 to use solar energy. That’s before any tax incentives and rebates.
How much energy your panels will generate, and thus, how much you save on your utility, depends on several factors. You can determine the approximate output of your system by using an online calculator.
Learn The Rebates And Incentives In Your Area
Not only is the price of solar technology dropping across the nation, but a host of incentives and rebates exist that make using energy from sunlight a more attractive economic proposition. These incentives include the federal solar tax credit, state tax credits, solar renewable energy certificates, and cash rebates offered by municipalities, states, and utility companies for property owners who install PV panels. Availing of those incentives will help reduce the costs of your solar energy system.
Compare Costs Vs. Savings And Returns
Does a solar panel system help you save money considering the hefty capital you’ll spend on your modules? To determine if going solar will make sense for you, you’ll need to consider how much you pay for your electricity bills and compare it with the cost of a solar system.
Let’s say you spend $100 per month on electricity. Adding that amount for 30 years means you shell out over $60,000 on electricity. That’s assuming that power rates don’t spike within that time frame.
Meanwhile, a solar power system costs between $11,000-$14,000 after the federal tax. Divide that by the average lifespan of the PV modules, which is around 20-25 years, and you can easily see why many consider solar a wise investment.
FAQs
What type of energy is solar power?
Solar power is considered a clean and renewable type of energy. It’s clean because a solar panel produces solar electricity without emitting greenhouse gases that harm the environment. Meanwhile, a PV system gets its power from the sun, an inexhaustible source, making solar a renewable form of energy.
How many solar panels does it take to run a house?
On average, a typical US home needs around 20-25 solar modules to cover its electricity consumption fully. But that number may vary due to several factors such as the panels’ efficiency, the amount of sunlight in your area, and your energy usage.
What is the catch with free solar panels?
Because one deterrent to going solar is the energy system’s cost, getting solar panels for free might seem like a dream come true for those who want to switch to solar power. But before rushing off to avail of the offer, you need to understand that although the solar company will install the modules at no upfront cost to you, the energy system is not exactly free.
Installers who advertise free solar panels are actually talking about solar financing options, such as Solar Power Purchase Agreements (PPA) and solar leases. With both agreements, the solar company will install the system without any cash outlay from you. However, you’ll have to pay for the electricity that the modules will generate.
In effect, the panels are free, but the energy they produce isn’t.
Does weather affect the production of solar energy?
Yes, the weather does have an impact on the output of a solar energy system. On a cloudy or rainy day, the panels generate 10 to 25 percent less electricity than when the sun is shining brightly.
Rain doesn’t affect the production of the modules, but snow can lower the panels’ production if it accumulates on the modules and prevent sunlight from reaching the PV cells inside.
Still, expert solar installers will know how to work around the problems posed by the weather on your solar panel system.
Final Words
Although at first glance, going solar seems like a financially daunting proposition, it has its advantages. If you compare the price you pay for your utility over time with the money you save by getting free energy from the sun, you can easily see why it is still more beneficial to take advantage of this clean and renewable energy source.
Keep in mind that solar panels usually last over 25 years. During their lifetime, they will produce energy without the harmful emissions associated with electricity that comes from traditional sources. Using a solar energy system, even just the average 5 kW one, means you’ll eliminate around 25,000 pounds of carbon emissions that will otherwise go into the atmosphere. Imagine the vast benefits that will bring to the environment.
Updated on
