40 Fun & Fantastic Solar Power Facts You Might Not Know About

The sun is a remarkable energy source. If harnessed, an hour’s worth of sunlight that strikes the earth is enough to meet the world’s electricity needs for a whole year. That’s how much power the sun packs. But there are still many things about solar we don’t know or understand. So let’s take a look at some of the fun facts about solar energy and find out how we can benefit from it.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the free energy that comes from the sun. When captured, we can use the radiant power from the sun’s rays to generate electricity for our homes. Because of the many advantages this power source offers, it is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy in the United States.
1. It’s Totally Free, Unlimited and Doesn’t Produce Any Noise
All that power from the sun is free. And while power plants or even other renewable energy sources like wind turbines produce noise when generating electricity, the photovoltaic effect creates electric power without making any noise.
2. Producing solar energy results in zero pollution or adverse environmental effects.
A solar panel absorbs the sun’s energy and turns it into electricity without emitting any greenhouse gases or particulates that warm the planet or pollute the environment. In contrast, electricity produced from burning fossil fuels spews tons of carbon emissions into the air. In 2019, 74% of the country’s total greenhouse gas emissions came from fossil fuel combustion.
3. It’s the Most Widely Used Renewable Energy Source Because of its Reliability.
Solar modules have no moving parts, so they rarely break down. Moreover, they’re backed by substantial warranties, which ensures you won’t experience too much hassle if they malfunction. This makes a solar power system more reliable than the power grid.
4. It’s Perfect as a Temporary Energy Source.
Installing solar panels helps make homes and businesses more energy resilient. When power outages occur due to extreme weather or grid instability, the solar energy system can continue delivering electricity as long as the sun shines.
It’s also a preferred power source when energy is needed for a limited duration, such as in mining sites, fairs, and other events.
5. Solar cells can be bought per watt.
Solar modules are priced per watt, ranging from $0.70 to $1.50 per watt.
The History of Solar Energy
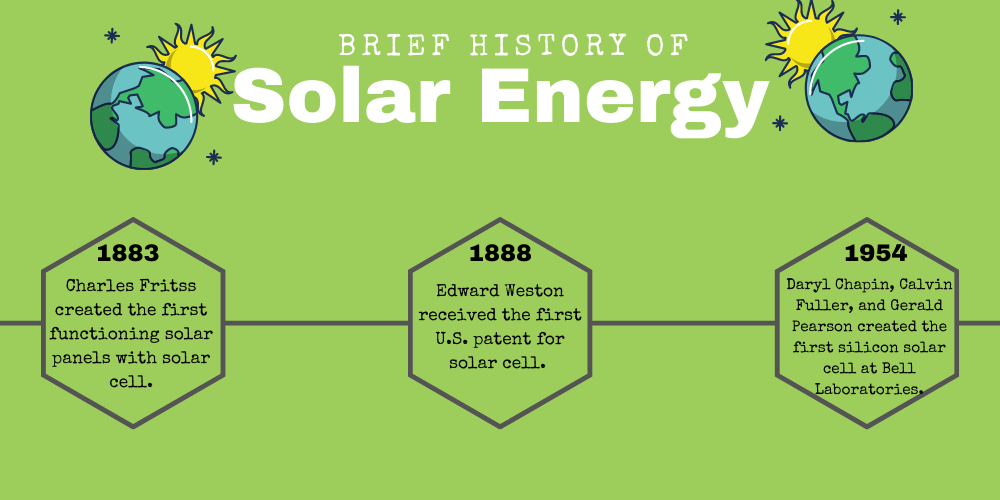
6. In 1954, Bell Laboratories built the very first solar cell.
In 1883 Charles Fritss coated selenium with a thin layer of gold and created the first solar cell. But the very first silicon solar cell came into being in 1954, created by the combined efforts of Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson, at the Bell Laboratories.
7. Bertrand Piccard flew a solar-powered plane around the globe in 2016.
The Solar Impulse 2 circumnavigated the earth in 2016, piloted by Bertrand Piccard and Andre Borschberg. The journey took over 500 days, with the plane flying at an average speed of around 45 mph (70 kph). Solar Impulse 2 is the first aircraft to fly around the world using only the power of the sun.
How Does Solar Energy Work?
8. Solar power is measured similarly to electricity.
Like electricity, solar energy is measured in watts, where 1 kilowatt (kW) equals 1000 watts (W).
9. Solar panels don’t need direct sunlight to produce electricity.
Maximum solar energy production occurs when the sun is shining brightly. However, even without direct sunlight, PV modules keep generating electricity. That’s because they produce energy by absorbing the photons that are available in natural daylight.
10. Solar panels are made of photovoltaic cells.
The photovoltaic cells capture photons or light rays, which causes a reaction between the protons and electrons in the cells. This reaction leads to electricity generation.
11. Photovoltaic cells are mostly composed of different types of silicon.
The types of silicon used in PV cells are single crystalline, multicrystalline, polycrystalline, or amorphous. They’re differentiated by their semiconductor’s crystal structure.
Solar Energy Efficiency
12. Solar energy is a lot cheaper than fossil fuels.
The Solar Energy Industries Association states that solar energy is more cost-effective than traditional power sources, even without government subsidies.
Natural gas, the cheapest fossil fuel, costs around 4.2 to 7.8 cents per kWh. Compare that with solar energy that costs 4.3 cents and can eventually drop to 3 cents per kWh.
13. An entire household rooftop’s solar panel system can lower pollution by 100 tons of carbon dioxide.
Because PV panels generate electricity without releasing harmful gases, an average residential energy system can meet the entire house’s power needs with 80% fewer carbon emissions.
14. Solar power is free, and maintaining installed photovoltaic panels is minimal, so returns are high.
Solar panels’ lack of moving parts minimizes breakdowns, and warranties take care of repairs and replacements. On top of that, you can enjoy financial benefits from going solar, such as when your utility offers a net metering option. With net metering, you can reduce the amount you pay your electric utility.
15. Homeowners who want to use solar power don’t have to install solar panels on their property.
Some homes may not be able to accommodate solar panels, like when the roof area is too small, or the property is under considerable shade most of the day. Still, you can use the energy from the sun if you want.
Community solar is a facility that multiple subscribers share. The solar panels and other equipment are set up in a central locality, eliminating the need for individual households to put installations on their roofs. The members of the solar community share the cost of the hardware and the power produced by the system.
16. Most solar panels have a capacity of 200 to 250 watts, and can produce eight to ten kilowatts of energy per square foot.
On average, US households consume around 11,000 kWh of electricity a year. So if you aim to live off the grid, you’ll need at least 30 PV panels with 250-watt capacities to fill your energy needs. That’s assuming you get 4 hours of full sunlight a day.
17. Investing in solar energy will usually yield a 100% ROI in five to 15 years, but Americans have reached the break even point in as short as 3 years.
It usually takes around 15 years to pay for the cost of a PV system. However, because the price of solar has plummeted while grid-sourced electricity rates continue to skyrocket, homeowners are reaching the break-even point earlier. The payback period is now down to around 8 years. Still, some solar consumers in states with high electricity rates see break-even points after only 3 years of using solar energy.
18. To power the entire globe with solar energy, we would need to install solar panels on 191,000 square miles of land.
As of 2020, the entire globe needs 3 trillion watts of power. To provide that amount of solar energy would require 51.4 billion 350W solar panels that will occupy 191,000 square miles of land.
Solar Power by Country and City
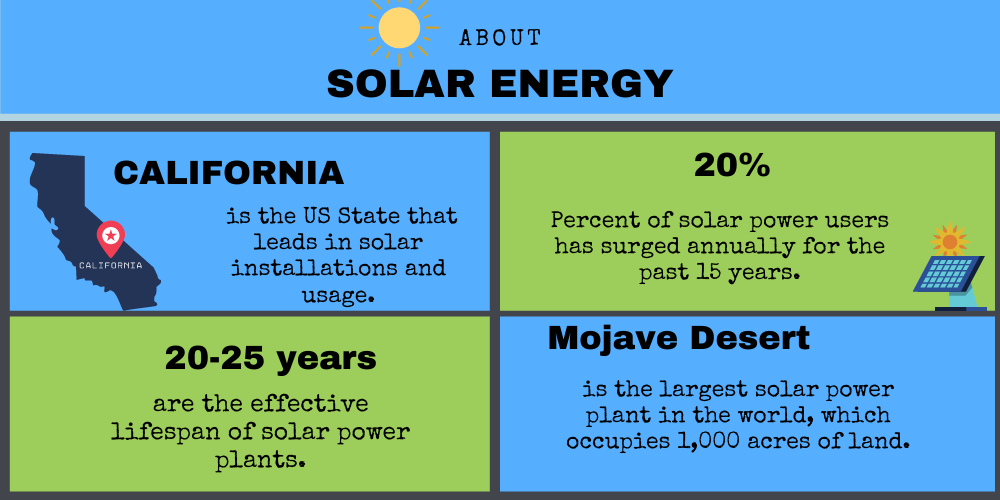
19. The largest solar power plant in the world is in the Mojave Desert in California, which occupies 1,000 acres of land.
The Ivanpah Solar Power Facility is the world’s largest operating solar thermal energy plant. It was deployed in 2014 and, using concentrating solar power (CSP) technology, it has a gross capacity of 392 megawatts (MW). CSP involves the use of mirrors to harness the sun’s energy.
20. The top four countries that favor and use solar energy are Japan, Germany, the United States, and China.
With 205 GW of installed solar capacity at the end of 2019, China leads the way among the top 4 nations that use the sun’s power for its electricity requirements. The US ranks second (76 GW), followed by Japan (63.2 GW) and Germany (53.7 GW).
21. California is the US State that leads in solar installations and usage.
California tops the list for US states that deploy solar energy with 21 GW of installed solar capacity. North Carolina is a far second with 4.3 GW.
22. Las Vegas is the largest city in the US that operates wholly on renewable resources.
Las Vegas started the shift to renewable energy way back in 2008, cutting its electricity usage by more than 30 percent. Today, Las Vegas is the largest city in the country that relies entirely on renewable energy for its power needs.
23. Since early 2019, the US has installed over 2M solar systems.
Solar installations across the nation breached the 2 million mark at the end of 2019, totaling around 71.3 GW of solar capacity and producing over 100 terawatts of electricity.
The figure is expected to double by 2023.
24. Several states allow selling excess solar energy produced.
States with net metering policies allow consumers to sell their PV modules’ excess electricity to their utility. In return, solar users get credits, which they can use to offset the electricity they draw from the grid.
25. Incentive programs exist in many different states.
> that offer rebates and coupons for solar panel installation, encouraging people to switch to a more sustainable source of energy.
Several states offer various incentive programs to soften the financial brunt of installing a solar system. These incentives include tax credits, upfront cash rebates, solar renewable energy certificates, and performance-based incentives.
26. As of 2016, over 260,000 Americans work in the solar energy industry and is expected to increase to 360,000 by this year.
Industries involved in zero-emission technologies provided employment to around 611,000 people in 2019, with over 260,000 working in the solar industry. The pandemic led to a drop in employment opportunities, but the numbers are starting to rise again. To reach 100% reliance on clean energy by 2035 will require 900,000 workers.
Solar Energy Tax Benefit
27. Solar panels are property tax-exempt and can increase a home’s appraised value.
Several states allow homeowners to exempt the increased value that a PV system adds to their property when computing their taxes. Homes will solar modules typically gain a premium of around 4.1% on their resell price.
28. Buying solar panels make the homeowner eligible for a 30% tax break from the federal government.
Up until 2019, the Federal Solar Tax Credit lets you deduct up to 30% of the cost of installing a solar energy system in your home. There is no limit to the value of the system installed. So whether your PV array is worth $10,000 or $30,000, the tax break is available to you.
However, the Federal Solar Credit has started to step down. From 30% in 2019, it now stands at 26% until 2022. It goes further down to 22% in 2023.
Uses of Solar Energy
29. The use of Solar power has surged at around 20% annually over the last 15 years.
Despite minor setbacks due to the pandemic, the deployment of solar energy continues to surge, driven by rapidly declining prices and improvement in panel efficiencies. Over the past decade, the adoption of solar technology keeps rising at an average of 20% a year.
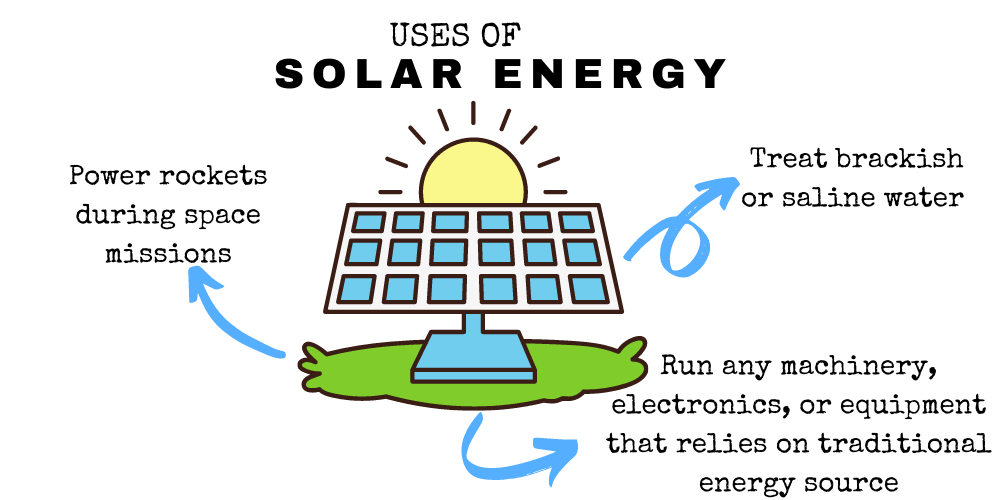
30. It’s used to treat brackish or saline water to make them potable.
Brackish or saline water contains substantial amounts of dissolved salts which makes it unsuitable for drinking. Desalination is one of the ways to make this type of water drinkable. Desalination devices powered by solar energy turn salt water into fresh drinking water, which can help address the world’s water crisis.
31. It can power any machinery or equipment that’s powered by fossil fuels.
Being an alternative energy source, solar energy can run any machinery, electronics, or equipment that relies on traditional energy sources. All it takes is using suitable solar technology.
32. It’s been used by various countries to power their rockets during space missions.
The Vanguard 1 is the first satellite that utilized solar cell power. Launched in 1958 by the United States, it is the oldest satellite that still orbits the earth.
Solar Power Plants
33. Solar power plants use a concentrated amount of heat from the sun to power steam turbines that generate electricity.
They have reflectors or mirrors that harness and focus the sun’s rays into a receiver which then heats water to produce steam and power turbines. In turn, the turbines produce electric power.
34. Solar power plants have an effective lifespan of about 20 to 25 years.
Solar panels don’t last forever, but they have a long lifespan, lasting as long as 20-25 years. Power plants, however, stay far longer. When the infrastructure for the solar plants is in place, the panels, which degrade over time, can be easily replaced, usually with newer and more efficient models.
35. Solar power plants can be built and deployed quicker than any other energy source.
Installing a ground-mounted solar usually takes around 3 months per MW. In contrast, the construction time for a nuclear power plant range between 50 to 200 months, while a coal-fired power plant takes roughly around 4 years to build.
36. Target, Walmart, and Apple are the most notable corporate buyers of solar energy.
These companies are making significant investments in solar energy. In 2019, Apple led the way with an installed capacity of 398.3 MW. Walmart has 331.0 MW while Target has 284.8 MW.
Solar Energy Storage
37. Thermal storage methods can trap solar energy in materials like stone, earth and water, and molten salts.
Thermal storage systems store heat or cold for later use. Materials like stone, earth, water, and molten salts absorb heat, making them excellent storage mediums.
38. Storage systems enable the use of solar energy all day and all week.
Though solar energy tends to be intermittent, storage systems make it possible to store the excess production of the PV modules. With a large enough battery, you’ll have enough solar power to draw from during times when your panels’ output can’t meet your energy demands.
Disadvantages of Solar Energy
39. It won’t work at night and terrible weather will make it unreliable, especially if it operates without storage capability.
Solar cells need natural daylight to generate electricity. That means they cease production at night. During inclement weather, they may continue producing energy but at a much lower capacity. Without a battery system in place, you can’t rely on your PV system 24/7.
40. Solar technologies require hectares of land to collect solar energy for use of a massive public.
Utility-scale PV systems require 3.5 to 10 acres per megawatt while concentrating solar power facilities need anywhere from 4 to 16.5 acres per megawatt.
FAQs
How many solar panels does it take to run a house?
With an average consumption of 11,000 kWh a year, it will take around 30 solar modules with 250-watt capacities to power a home.
What’s the catch with free solar panels?
Advertisements regarding free solar panels usually refer to financing options for a solar energy system. These options include solar leases or solar loans where the solar company will install the panels for free, but you’ll have to pay for the energy they generate.
What are the 5 benefits of solar energy?
1. Using solar energy brings the following advantages.
2. Reduction in electricity bills
3. Lowered carbon footprint
4. Increase in home value
5. Tax breaks and rebates
6. Energy resiliency
How much does it cost to start a solar farm?
A 1 MW utility-scale solar farm will require roughly around $1 million to install.
How much do solar companies pay to lease your land?
The amount varies from project to project but on average, solar lease rates fall between $700 to $3,000 an acre.
Updated on
