Monocrystalline vs Polycrystalline Solar Panels
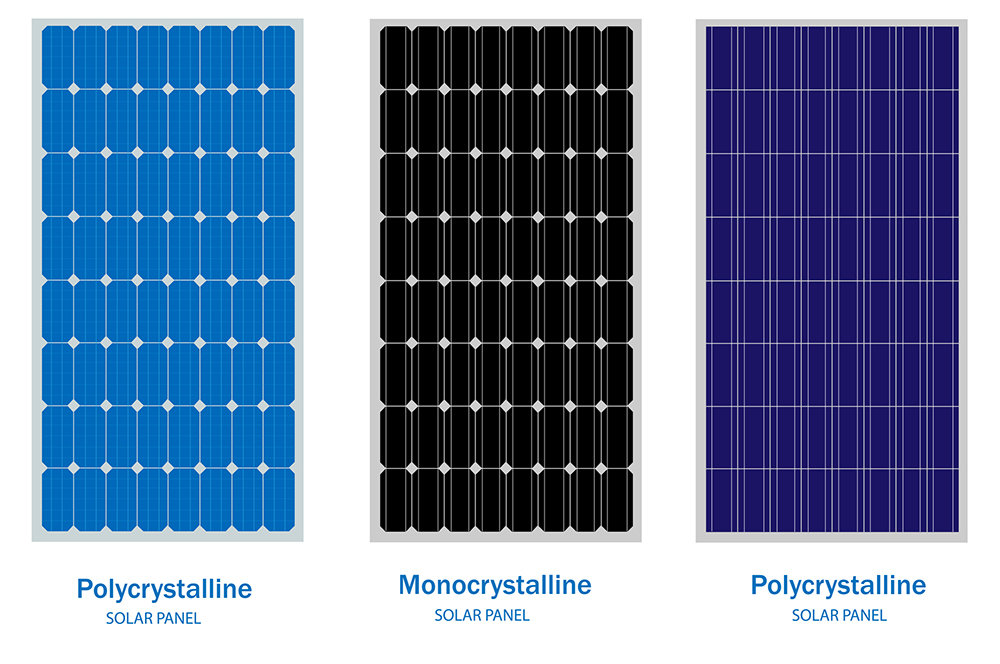
There are two basic types of solar panels: Polycrystalline solar panels and monocrystalline solar panels. Although polycrystalline panels are more popular, they may not always be the best option. Read on to learn about both pros and cons of both types of solar panels.
First things first, many US households have decided to invest in a solar energy array. As there are many different homes and uses for solar panels, over time, many different kinds of panels emerged as well. Monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels are the most popular, while the market is seeing a rise in flexible solar panels as well.
What is a Solar Panel?
A solar panel is a device that generates electricity. Each solar panel is made up of many solar cells, which interact with direct sunlight to excite electrons found within. This creates the current that is then taken to the inverter. The inverter turns this DC (Direct Current) electricity into AC (Alternating Current) electricity that the appliances and devices around your home can use.
As each solar cell can only produce a small quantity of electricity, many of them are combined into a single solar panel. Solar panels can produce much more current – around 350 Watts for an average roof-mounted solar panel. Many of them can be combined to produce more power – as much as you need.
An average home solar system usually produces 4-6 kW of electricity when exposed to direct sunlight. Large-scale solar farms can produce upwards of 100 MW, or 100,000 kW of electricity, and can supply power to thousands of households at the same time. Combined with a large-scale solar storage solution, such as batteries or pumped hydro, they can also supply power during the night. Combined with a net-metering in place, they can serve you overnight as well.
Types of Solar Panels
Over time, as solar power technology evolved, we got different kinds of solar cells – always made of silicon wafers. Today, there are two basic kinds of solar panels: monocrystalline solar panels and polycrystalline solar panels. There is also one more kind, thin-film solar panels, although their low efficiency makes their use limited.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
The most efficient panels are monocrystalline solar panels. A typical monocrystalline panel has several solar cells, all arranged so as to cover as much space as possible. They are called monocrystalline because each solar cell is made of a single silicon crystal. They are known for their high efficiency, of around 18%, and are currently the most efficient type of solar panels.
In the world of solar panels, monocrystalline solar panels are considered a premium solar product – they are highly efficient, stylish, and last a longer time than most polycrystalline solar panels. Monocrystalline solar panels tend to last over 25 years, while polycrystalline solar panels last around 20-30 years.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline panels, on the other hand, are a bit less efficient – usually 14-16%. Although this is a bit lower than with mono panels, they are cheaper and may pay off faster. Investing in poly panels will reduce your initial costs, but some people find the bluish color of the panels unattractive, especially if placed on a red rooftop. Nevertheless, they are very good and reliable. Research has also shown that poly panels may perform a bit better during overcast days or when they are covered in a thin layer of snow.
Thin Film Solar Panels

Thin film solar panels have different types of cells when compared to traditional solar cells. Here, solar technology allows the cells to be flexible and to be able to be wrapped around different objects. This is done by printing or applying a thin layer of photovoltaic material on top of a glass or plastic material.
In the latter case, the plastic base allows the panel to be bendable. They are a perfect solution that is applied to roof tiles or other objects of irregular shapes, such as your RV rooftop. Some people even make them into rollup shades that can be opened as soon as you park your RV.
Thin film solar panels are less efficient than mono panels or even poly panels. Nevertheless, their lower efficiency is compensated by a lower price. If you would like to provide energy for your home, you could do that by means of thin-film solar panels, although you would need a larger rooftop surface to do so. If space is of the essence, you should probably opt for poly solar panels or even mono panels. Covering every square foot of your home in solar panels may not be the best option, aesthetically speaking.
Difference Between Monocrystalline & Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Mono panels vs polycrystalline solar panels – what is the difference? As we stated before, the difference is in the type of solar technology that is used in manufacturing these two types of solar cells. The electricity generated is always the same, although the voltage and amperage, as well as wattage, can be different. As most solar professionals will tell you, using a lower number of more efficient solar panels is the best option for many, but the opposite holds true for many as well.
When comparing monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, you should consider:
- The manufacturing process,
- The price,
- The efficiency,
- The lifespan,
- The temperature coefficient, and
- The aesthetics.
Some experts would also add performance under stress to the list, although this is not always an important factor. We will consider them all.
| Comparison Factor | Monocrystalline | Polycrystalline | Thin-Film Panels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | High | Middle | Low |
| Efficiency | High - +15-20% | 13-16% | 7-18% |
| Lifespan | + 25 years | ~ 25 years | 10-20 years |
| Temperature Coefficient | High | Middle | Low |
| Appearance | Black - stylish | Blue - good for seaside | Dark Blue to Black |
Manufacturing Process
The main difference between mono vs poly solar panels is in the manufacturing process. All other differences there is the result of the fundamental difference in how they are made. While solar manufacturers use one silicon crystal to form single-crystal silicon cells (monocrystalline panels), the shards that are left over are fused together to make polycrystalline panels.
When making a monocrystalline solar panel, manufacturers melt silicone and place it in a mold. Once the crystals are formed, they are cut and shaped. This is how a single-crystal solar cell is formed. Because they are uniform in structure, they allow for an easy passage of electrons and can allow a higher efficiency, and, ultimately, a higher price.
All the leftover crystal pieces and shards are fused together. This is how polycrystalline solar cells are made. Connecting many of them in a single structure gives you a polycrystalline solar panel. Polycrystalline cells do not have a uniform internal structure. For this reason, multiple silicon crystals in a single solar cell allow fewer electrons to move around and allow for lower efficiency. This is the reason why polycrystalline panels are cheaper than monocrystalline panels.
Besides this, the manufacturing process can also allow for some other changes to the panels. Half-cut solar cells, for example, have a higher efficiency than their uncut counterparts because they tolerate partial shadowing better. Likewise, installing microinverters is also done during the manufacturing process. Hotter climates, with more sunshine, will demand monocrystalline, so take this into consideration.
Price
As we’ve mentioned before, the technology used in the manufacturing process dictates the efficiency and the price of solar panels. As they do not come cheap, the US government and state governments offer significant rebates and other incentives to ensure that the technology is widely adopted. If the price is still too high, there are other ways to get solar panels. Financing, solar loans, and signing a power purchase agreement (PPA) are some common ways to get almost-free solar panels.
Efficiency
Depending on the efficiency of the solar cells, the overall efficiency of the solar panel and the solar array can be higher or lower. In general, monocrystalline panels are more efficient than polycrystalline panels, while at the same time, they can be more efficient even with partial shading. On the other hand, the monocrystalline panels are less prone to suffer efficiency losses due to temperature rises.
Monocrystalline panels in general feature efficiencies of 15-20%. Polycrystalline panels, on the other hand, are 13-16% efficient, and they are likely to be a better solution for more households. However, if you are limited in roof space, live in areas where high temperatures are not common, or can even sell leftover electricity on the residential market, you are better off with monocrystalline panels.
LifeSpan
The lifespan of monocrystalline solar cells is different from that of polycrystalline solar cells. For this reason, mono solar cells will easily outlive poly solar cells. The lifespan of mono panels is over 25 years and around 25 years for poly panels. When speaking of the life span of solar panels, it is useful to notice that the usable lifespan of these panels is considered a period in which they keep around 80% of their energy generation capacity and can therefore offset your high energy bill.
Temperature Coefficient
The energy output even of the best solar panels depends on outside factors, such as temperature. The efficiency of solar panels depends on this factor. Very low and very high temperatures affect energy production. High summer temperatures, for example, can significantly reduce how much energy is produced at any given moment in time. Monocrystalline solar panels are more resistant to high temperatures, and their energy efficiency is slower to degrade with an increase in temperature. This means they have a higher temperature coefficient.
Aesthetics
Yet another factor to consider before making your final purchase is the aesthetics of your solar panels. As the looks of your home play a considerable role in how well you feel in your home, you should know that many people find polycrystalline solar cells and panels to be less attractive than their mono-counterparts. This is because black combines better with any color and shape than a dark blue hue can. In any case, every solar panel has a lot of benefits to the environment that you should consider.
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Solar Panel
Now that you know how to differentiate monocrystalline vs polycrystalline solar panels, it is time to see which type works better for you and your energy needs. Here, there are many factors to consider before making your purchase. In general, you want to pay attention to:
- Your individual preferences,
- Your space limitations, as RV solar panels, will be different from the panels you install in your home,
- The amount of dust, snow, and shade you can expect in your region,
- The climate of your region, and
- Your solar financing options.
Individual Preferences
When it comes to individual preferences, many people focus on color. And while polycrystalline panels and their bluish hue may look better at the seaside, the mono panels, and their distinctive black color, will look better in almost all other settings. Considering that mono panels also last longer and can produce much more electricity over their lifespan, they are also a better choice for all who would like to invest for the long term.
Space Limitations
Space limitations can also dictate what kind of panels you should put on your roof. If the space is limited, you should go for monocrystalline panels, as every square foot of your rooftop that is under panels will be producing up to 35% more electricity than polycrystalline solar panels. Monocrystalline solar panels are also a much better option for multi-story homes and RV applications.
If, on the other hand, you live in a large home with plenty of rooftop space compared to the square footage of your home (such as single-story houses), you should consider purchasing more polycrystalline panels. This way, you will be able to save money by sacrificing some more rooftop space. Thin-film solar panels should not be forgotten either, especially in RVs, as their blanket-like flexibility is perfect for all the imperfections in the RV roof shape.
Amount of Dust, Snow, and Shade
The amount of dust, snow, and shade that your panels receive will also influence the type of solar panels that you should place on your rooftop. Monocrystalline solar panels are better suited for dusty climates and climates with a lot of snow. Likewise, they can better tolerate partial shade, especially if you purchase half-cut models.
Snowy regions also prefer mono solar panels. During the winter, they heat up faster and can produce more energy during the colder part of the year. Furthermore, as they are darker and heat up faster, they will melt any snow that may accumulate on top of them and will be ready for energy production in no time.
Climate
The climate you live in is also a factor to consider before purchasing your solar panels. If you live in very hot or very cold regions, you should go for mono solar, as every polycrystalline panel is more sensitive to temperature fluctuations and will result in lower overall energy production. Living in a humid climate, on the other hand, can both lower and increase energy production. While clouds reduce the amount of light that hits your panels, the rain will clean them and make them more energy efficient.
Solar Financing
The final thing to consider is solar financing. Although panels have become much cheaper recently, installing even a polycrystalline silicon PV array, or fewer panels of the monocrystalline type can still be a significant expenditure. The US Federal Government offers significant tax credits, up to 26% of the initial investment cost.
This tax credit can then be combined with other incentives and rebates, such as those offered by your state or even your utility company. Being aware of these incentives can save a lot of money for you and can help you increase the size of your solar array to the size you actually need. You can ask in your local municipality office or even a solar professional to learn more about how you can benefit from solar financing.
In addition to these programs, you can also go for a solar loan with your bank. If you have a suitable flat surface and sufficient income, any bank will help you by offering a solar loan. Many banks, in cooperation with the local authorities, will even offer a zero-interest solar loan to all that are eligible.
Solar PPA is another form of solar financing that you should consider. Under this format, you sign a Power Purchase Agreement with the installer or even a utility company. Under this agreement, you purchase all electricity that the panels produce. What is great here is that you get a heavily discounted rate. On the other hand, your electricity bills will be the highest during the summer, while your winter bills will be much lower. This is a great way to balance your energy expenditure.
Other Solar Panel Technology
Besides monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon PV cell technology, the market and investments have brought about many other types of solar panels to the market. With this in mind, we will consider some of the most popular alternative solar panel technology:
- Flexible solar panels,
- Passivated emitter and rear cell panels (PERC),
- Half-Cut panels,
- Bifocal solar panels,
- Transparent solar panels, and
- PV shingles.
Flexible Solar Panels
Flexible solar panels or thin-film panels are very thin solar panels. They are made by printing silicon crystals onto a plastic surface, which acts as the structural support. As they are thin they are very flexible. This enables them to be applied to any surface that you have available, even if the surface is off-shape or otherwise irregular.
Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell [PERC]
Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell is a solar panel technology that introduces an additional layer of material into the panel itself. The added layer is highly reflective so that all the light that goes through the panel is reflected back, getting another chance to be absorbed. The main advantage of this type of panel is that the layer adds a lot of efficiency to it with little added cost.
Half-Cut Cells
Half-cut cells are monocrystalline types of PV cells that use an entire silicon crystal that has been cut in half. The main advantage of this type of PV cell is its higher resistance to partial shading, where only a portion of the solar cell is nullified and produces no electricity. Theoretically speaking, this type of technology should cut power losses due to shading by as much as 50%.
Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels are somewhat similar to PERC solar panels. In these, the passivation and reflection layer is substituted by another solar panel. The panels are usually of different kinds, so the primary panel may be monocrystalline, while the second panel may be polycrystalline. This is usually done to keep the expenses at a reasonable level. The biggest disadvantage of this type of panel is its added weight, which some roofs may not be able to support.
Transparent Solar Panels
Transparent solar panels, on the other hand, are a type of panel with a possible new application. Panels like this can be integrated into buildings, making the windows absorb sunlight and produce power. There is also another type of transparent solar panel, the so-called agri-voltaic panel, which consists of two layers of glass or sturdy plastic. In between them, there are standard solar cells, placed at a bigger distance from one another. This type of panel is being tested in Europe as a protection against the sun in agricultural applications. Current results show that the crops growing under them can produce as much as 30% more biomass.
PV Shingles
PV shingles, on the other hand, take a different approach to producing electricity on your own roof. Solar shingles completely replace your existing roof tiles and existing solar panels. They come mostly in black color, so they are very stylish. However, as the total surface solar cells take up is smaller than with a conventional panel, you will have to consider installing them on a larger surface.
FAQs
Which Solar Panels are the Most Reliable?
Monocrystalline solar panels are the most reliable on the market. As they are made of a single piece of silicon crystal, they are sturdier and more efficient than their polycrystalline counterparts. They also feature higher efficiency levels, so you will likely need fewer of them to satisfy your energy needs.
How to tell the Difference Between Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline?
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels are easy to tell apart: their color is different. Monocrystalline solar cells are black in color, while polycrystal lines are of a dark-blue shade. Besides this, they should be clearly labeled on the packaging, and monocrystalline panels will always have higher efficiency levels than monocrystalline.
How Long Do Polycrystalline Solar Panels Last?
Polycrystalline solar panels last up to 25 years. In reality, they can last even longer, but their efficiency levels will drop below their optimal 80%. After this happens, you can keep the same solar panel system on your roof, or you can sell them. There is also an emerging market for solar panel recycling, so, by the time their useful life is over, you will be sure they do not end up in a landfill.
Can you Mix Poly and Mono Solar Panels?
Yes, you can mix poly and mono solar panels. In this case, you should pay attention that there is no significant difference in their power output. If this is the case, the overall solar system may lose efficiency, although not to a large extent. You will still be able to produce power, but not as much as with a single type of solar panel. Furthermore, opting for a single kind of panel will make their installation, all the necessary calculations, and their removal and replacement much easier.
Conclusion
Solar panels are the future of energy generation. When it comes to choosing the right type of solar panels, this is a headache for today. We’ve researched different types of monocrystalline vs. polycrystalline solar panels so that you do not have to. Follow our guide and see which type of panels is best suited for your climate, energy needs, available space, and any other preferences you may have.
Updated on
