Top Electricity Generation Sources in Texas
From traditional sources like coal to up-and-comers like wind and solar, here’s how Texans get their electricity.
Though Texas led the country in oil production in 2016, it has also achieved impressive results with alternative fuels. These up-and-coming energy production leaders are on track to dominate electricity generation in Texas in the not-so-distant future. This could possibly improve Texas residential electricity rates and commercial energy rates.
The major sources of electricity in Texas include the following:
Natural Gas
Texas produced over 25% of the natural gas used in the U.S. in 2016, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)–making natural gas a cornerstone of the Texas economy. More than 25% of known natural gas reserves within the U.S. are located in Texas, says the Texas Office of the Governor. Natural-gas-fired power plants accounted for 162 of Texas’ 340 electric power plants in 2016, producing 50% of the state’s total electricity generation.
Wind Power
Among renewables, wind is the major player in Texas. In fact, Texas has led the country in wind energy for years, thanks to the strong winds of west Texas, says Scientific American. “Since 2014, Texas wind turbines have produced more electricity than both of the state’s two nuclear power plants,” says the EIA. Wind generated one-eighth of Texas’ total electricity in 2016, and at least 24,000 wind industry jobs exist thus far, making wind an increasingly key part of the economic landscape in Texas.
Coal
Coal accounted for 32% of Texas’ energy production in 2016. Lignite coal found in large belts in east and central Texas has historically accounted for much of Texas’ electricity-producing coal, as well as bituminous coal in other parts of the state. However, these plants are increasingly being retired as renewables become more competitive and coal less so. Shutting down some of the oldest coal plants tightens the coal supply and makes prices more competitive for the remaining ones, explains the Houston Chronicle.
Solar
While its solar capacity lacks the strength of its wind-powered electricity generation thus far, Texas plans to triple its solar production between 2018 and 2020. As of March 2016, solar already employed 7,000 people in Texas. Because there will be more tax credits for solar than wind in the coming years, expect to see solar investment ramping up.
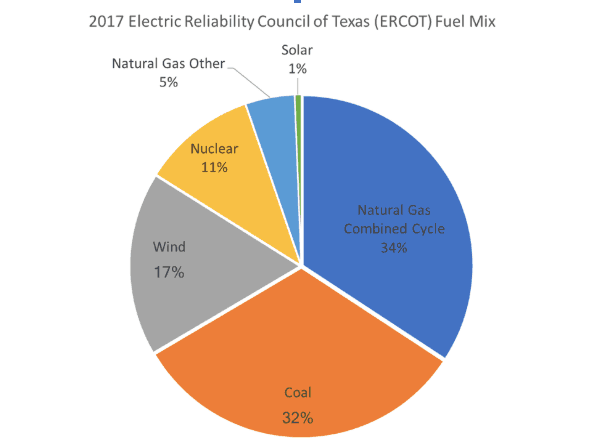
Nuclear
Nuclear power produced 9% of the total electricity in Texas in 2016, says the U.S. Department of Energy. Texas has two nuclear plants, which each have twin reactors, and exports about 2% of the electricity it produces with them. Plans are in the works to build several more nuclear power plants due to their cost-effectiveness and competitiveness in the market.
Other noteworthy facts about Texas’ energy production:
- Texas is the only state in the lower 48 to have its own electricity grid, run by the Electricity Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). Serving three-quarters of the state, the ERCOT grid doesn’t exchange large power amounts with other states. “The fact that Texas can’t exchange large amounts of power with other states makes its renewable energy integration achievements even more noteworthy,” says Scientific American.
- Texas consumes more energy than any other state, but more than half of that is used for energy production.
- Production of too much energy has posed a challenge for Texas in recent years! Since supply has far exceeded demand in recent years, high production levels have made it tough for many producers to compete, since the state government doesn’t set prices on electricity.
Updated on



